Hello everyone, this is Bella from ZHEJIANG WUMA DRIVE CO.,LTD. This year marks WUMA's 30th anniversary, and we've launched a series of articles to share with you. Today, we'll be introducing mechanical transmission forms.
1.Gear Transmission Gear transmission is the most widely used form of mechanical transmission. It offers high accuracy, efficiency, compact structure, reliable operation, and long service life. Gear transmissions can be classified into many different types according to various standards.
Gear transmission is the most widely used form of mechanical transmission. It offers high accuracy, efficiency, compact structure, reliable operation, and long service life. Gear transmissions can be classified into many different types according to various standards.
Advantages: Compact structure, suitable for short-distance transmission; wide range of applicable circumferential speeds and power; accurate, stable, and efficient transmission ratio; high reliability and long service life; can realize transmission between parallel shafts, shafts intersecting at any angle, and shafts with arbitrary angles.
Disadvantages: Requires high manufacturing and installation precision; higher cost; not suitable for long-distance transmission between two shafts; no overload protection.
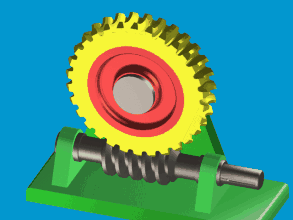
2.Worm Gear Drive
Suitable for motion and power between two spatially perpendicular but non-intersecting shafts.
Advantages: Large transmission ratio; compact structure.
Disadvantages: High axial force, prone to heat generation, low efficiency, can only transmit in one direction.
The main parameters of worm gear drives include: module, pressure angle, worm wheel pitch circle, worm pitch circle, lead, number of worm wheel teeth, number of worm threads, and transmission ratio.
3. Belt Drives
Belt drives are a type of mechanical transmission that uses a flexible belt tensioned on pulleys to transmit motion or power. A belt drive typically consists of a driving pulley, a driven pulley, and an annular belt tensioned between the two pulleys.
1) When used in applications where two shafts rotate in the same direction while parallel, it is called open-circuit motion, involving the concepts of center distance and wrap angle.
2) Belts can be classified into three main categories based on their cross-sectional shape: flat belts, V-belts, and special belts.
3) Key considerations in application include: calculating the transmission ratio, analyzing belt stress, and determining the allowable power of a single V-belt.
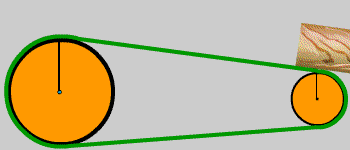
Advantages: Suitable for transmissions with large center distances between shafts; the belt has good flexibility, mitigating impact and absorbing vibration; slippage prevents damage to other components under overload; simple structure and low cost.
Disadvantages: Larger overall dimensions; requires a tensioning device; due to slippage, a constant transmission ratio cannot be guaranteed; shorter belt life; lower transmission efficiency.
4.Chain Drive
Chain drive is a transmission method that transmits the motion and power of a driving sprocket with a special tooth profile to a driven sprocket with a special tooth profile via a chain. It includes driving chains, driven chains, and ring chains.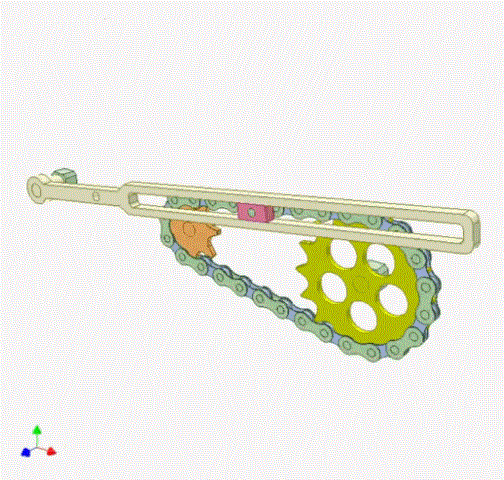
Advantages: Chain drives offer numerous advantages. Compared to belt drives, they eliminate elastic slippage and slippage, provide accurate average transmission ratios, are reliable, and highly efficient. They transmit high power, have strong overload capacity, and are smaller in size for the same operating conditions. They require less tension and exert less pressure on the shaft. They can operate in harsh environments such as high temperature, humidity, dust, and pollution.
Compared to gear drives, chain drives have lower manufacturing and installation precision requirements. Their transmission structure is simpler when the center distance is large. However, the instantaneous chain speed and instantaneous transmission ratio are not constant, resulting in poor transmission smoothness.
Disadvantages: They can only be used for transmissions between two parallel shafts. They are costly, prone to wear and elongation, and have poor transmission smoothness. During operation, they generate additional dynamic loads, vibrations, impacts, and noise, making them unsuitable for rapidly reversing transmissions.
5.Wheel system
A transmission consisting of two or more gears is called a wheel system. Based on whether there are gears with shaft motion in the wheel system, gear drives can be divided into ordinary gear drives and planetary gear drives. Gears with axial motion in the wheel system are called planetary gears.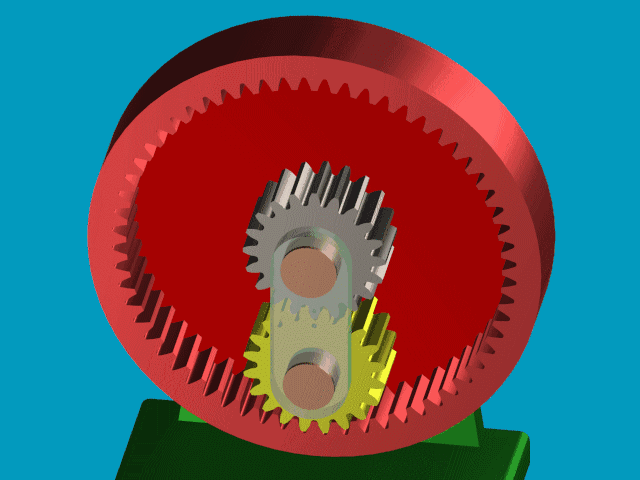
1) Wheel system are divided into two types: fixed-shaft wheel system and planetary wheel system.
2) The ratio of the angular velocity (or rotational speed) of the input shaft to the output shaft in a wheel system is called the transmission ratio. It is equal to the ratio of the product of the number of teeth of all driven gears in each pair of meshing gears to the product of the number of teeth of all driving gears.
3) In a planetary wheel system, the gear whose axis position changes, that is, the gear that both rotates and revolves, is called a planetary gear, and the gear whose axis position is fixed is called the central gear or sun gear.
4) The transmission ratio of a planetary wheel system cannot be directly calculated using the method for solving the transmission ratio of a fixed-axis wheel system. It is necessary to utilize the principle of relative motion and use the relative velocity method (or the reversal method) to transform the planetary wheel system into a hypothetical fixed-axis wheel system for calculation.
5)The main characteristics of wheel systems: Suitable for transmission between two shafts that are relatively far apart; can be used as a gearbox to achieve speed change; can obtain a large transmission ratio; can realize the synthesis and decomposition of motion.
If you would like to learn more, please feel free to contact us on our official website!
website: www.wumareducer.com
 Hot News
Hot News2026-02-24
2026-02-22
2026-02-20
2026-02-18
2026-02-16
2026-02-14